Just opened your eyes and can’t wait for your first cigarette of the day? If you’re lighting up without even thinking about it, maybe it’s time to start contemplating the harm that’s being done to your lungs. Emphysema is a progressive and irreversible lung disease. In 90% of cases, emphysema is caused by cigarette smoking. Continue reading “All about emphysema”
Tag: Lung diseases
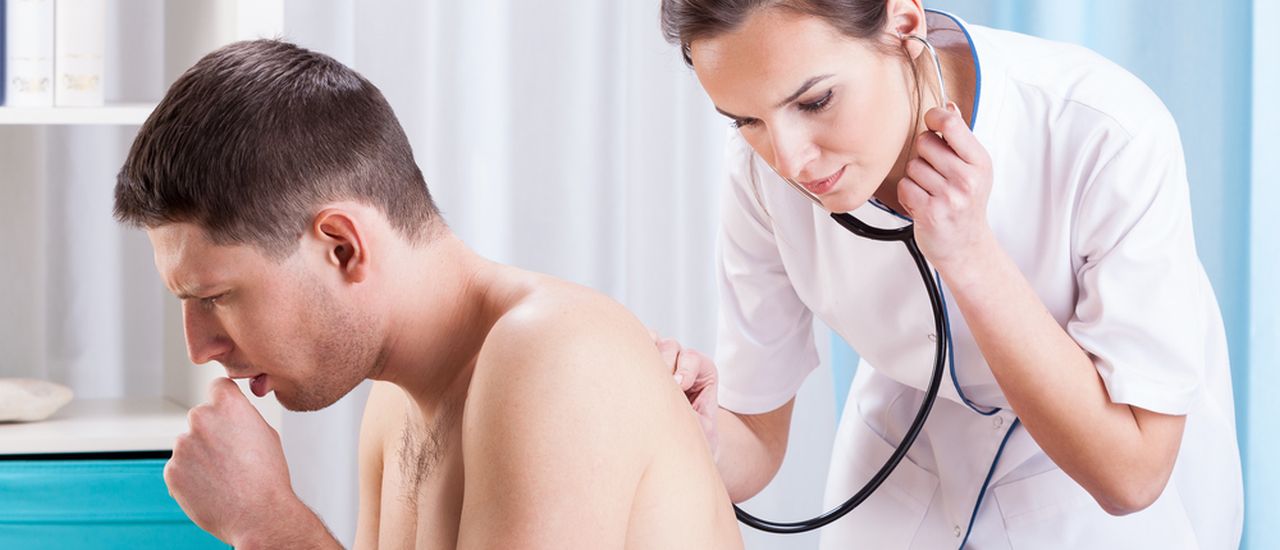
Coughing: How do you know if you have TB?
So, you’ve been coughing for a few months now and sweating at night… even your friends are saying you’ve lost some weight and should go for a TB test. TB is very common in South Africa, but fortunately it can be prevented and treated. Here’s what you need to know.
Preventing TB:
a) By the BCG (TB) vaccine:
- In countries where TB is common, the BCG forms part of the national childhood immunisation programme
- It’s generally used to offer children protection against TB
- It’s not used to interrupt the spread of TB from one adult to another
b) By preventing the spread of infectious TB from one adult to another. This is done by:
- Identifying people with active TB early on, and
- Treating them promptly with medication
TB is spread by airborne droplets, especially in crowded spaces. Here’s what you can do to prevent the spread of TB:
- Ventilate the house/room properly
- Cough, sneeze or laugh into a tissue and throw it away in a sealed plastic bag
- Wash your hands after coughing or sneezing
- Sleep alone in your own room
- Do not attend school or work until a healthcare worker has declared it safe to do so
- Avoid close household contact with children under 5 years old
- Take all TB medication correctly for the correct length of time
- Go for regular follow-ups and tests, to check if the TB medication is working and to see if it’s still infectious
- Avoid crowded places
Tests for TB:
Deciding if a person has TB or not, depends on many things:
- Symptoms suggestive of TB
- A clinical suspicion of TB in a patient (by a trained healthcare worker)
- TB screening tests such as:
- Microscopy (examination of stained sputum smears under a microscope)
- Culture (sputum culture of the TB organism; a process which takes longer)
- PCR-based tests/molecular testing
- Other tests including: chest X-ray, tuberculin skin test, blood culture, ultrasound, histological examination of tissue, amongst others
Treating TB:
The most important aspect of treatment is to take the correct medication for the correct length of time.
- TB drugs – the essential TB drugs are given in different combinations according to different treatment regimens
- Some TB drugs are bacteriocidal (killing action), bacteriostatic (sterilising action) or have the ability to prevent resistance
- The most common drugs are: isoniazid, rifampicin, pyrazinamide, ethambutol, streptomycin
- Other TB drugs are used in specific circumstances
- Some additional drugs include steroids and Vit B6
Common side effects of TB drugs include:
- Joint pains
- Nausea, loss of appetite, abdominal cramps
- Burning, numbness or tingling of feet (and hands)
- Orange/red discolouration of urine
- Skin rash or itching
If you’d like more information about TB or TB medication, please chat to our doctors on the Hello Doctor app.